In case you missed their recent announcement about Flash, Google and Adobe have teamed up on a new algorithm to index text content in Flash. As a result of the new algorithm for Flash, Googlebot now indexes “textual content in SWF files of all kinds” and extracts URLs embeded in Flash.” On July 1, 2008, Google rolled out another update designed to assist Googlebot in its ability to traverse simple JavaScript, like SWFObject. While the full impact is not yet known, these technologies will redefine how Flash sites are created, constructed, designed and, as a result, optimized.
Before discussing the results of my case studies and how to optimize an actual scenario Flash site, it’s important to understand some crucial background information.
Prior to the introduction of Google’s Flash algorithm, Googlebot crawled only (X)HTML architectures without executing JavaScript to access text content and/or URLs in Flash. These new capabilities raise a number of questions about how Google handles, crawls and indexes content in Flash. Does Google index all text content in Flash? Does Google associate text content in Flash with the correct parent URL? Does Googlebot crawl links containing “pound signs” in URLs? Can Flash files have PageRank? How does Google treat underlying interlinked (X)HTML structures of corresponding text content pages? What about “Progressive Enhancement” techniques? To answer these and other questions, I’ve been testing the effectiveness of “Google’s Flash algorithm” since its inception to find out what it means for current design practices.
Googlebot Flash Update Case Studies
Before looking at how to optimize an actual scenario site, it’s important to establish the new “laws of the land,” so to speak. For that reason, I’ve conducted a number of experiments with various sites but have included only a few case studies below. These case studies lay a foundation in terms of understanding how Googlebot now interacts with Flash since Google’s new algorithm for Flash was introduced. For demonstration purposes, I’ve used Google’s example from Google Webmaster Central Blog.
Google Flash Update Case Study #1:
Google Flash Content Association with Parent URLs
Experiment: To determine if Google associates text content embedded in Flash inside an (X)HTML page with the correct “parent” URL as a single entity.
Hypothesis: Google currently still does not associate text content in Flash with the correct parent URL or as a single entity.
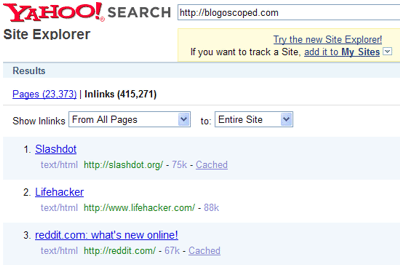
Background: According to Google’s Official Webmaster Blog, “If the Flash file is embedded in HTML (as many of the Flash files we find are), its content is associated with the parent URL and indexed as single entity.” To support their claim, Google posted the following image: 
Procedure: To test their claim, I used Google’s example query [nasa deep impact animation].
Result:
Conclusion:
Since the introduction of support for SWFObject in July, Google hasn’t associated text content in Flash with the correct parent URL or as a single entity. More often than not, either the Flash URL or both the Flash and parent URL are indexed.
*For test validity, I’ve monitored Google SERPs (search engine results pages) for the above query daily over a period of 60 days. I’ve also monitored Google’s SERPs for the following queries over the same period of time: [deep impact amy walsh] and [deep impact impact with comet Tempel 1].
Google Flash Update Case Study #2:
Google Flash File PageRank
Experiment: To determine if Flash files can accrue PageRank.
Hypothesis: Flash files can accrue PageRank.
Background: In a recent interview with Eric Enge, Maile Ohye mentioned that links in Flash function as a regular links and, therefore, can pass PageRank. If links in Flash can pass PageRank, it seems they could also accrue PageRank.
Procedure: Again using Google’s example, I visited both the parent and child URLs and recorded their “Toolbar” PageRank.
Results:
The (X)HTML parent URL page has a “Toolbar PageRank” of 7 while the Flash file URL (.swf) page has a “Toolbar PageRank” of 6.
Conclusion:
Flash files can accrue PageRank independent of their own parent URLs.
*Note: The illustration in this case study shows both the parent and child URLs indexed as unique individual entities in Google’s SERPs (search engine results pages). This further supports the findings in Case Study #1.
Google Flash Update Case Study #3:
Googlebot #anchor (fragment identifier) URL Extraction
Experiment: To determine how Googlebot handles URLs containing #anchors (fragment identifiers).
Hypothesis: Googlebot ignores #anchors (fragment identifiers) in URLs and, as a result, extracts only URLs preceding #anchors (fragment identifiers) in Flash embedded links.
Background: According to Google’s own JohnMu, “When we find URLs with an anchor attached like that (http://domain.com/page#anchor) we generally ignore the anchor part, since it is not relevant when fetching the contents of a URL.” While this is a convention commonly used for playhead control in Flash sites, it refers to the same page as defined by W3C.
Procedure: To test the experiment, I used Google’s “inurl:” operator to search for instances where Google had indexed a URL containing a pound sign. The queries I used are [inurl:#] and [inurl:& # 35;].
Result: No results found.
Conclusion:
Google Flash Update Case Study #4:
Google Flash Text Translation
Experiment: To determine if Google can translate text content in Flash.
Hypothesis: Google can not translate text content in Flash.
Background: “Google’s mission is to organize the world’s information and make it universally accessible and useful.” To some, “universal accessibility” would imply translation.
Procedure: To test the experiment, I used Google’s translation tool to translate the case study example into French, Spanish, Chinese, Arabic and Russian.
Result: No results found.
Conclusion:
Currently, Google doesn’t seem to support translations of text content in Flash.
Googlebot Flash Interaction Scenario
Avenues for optimizing Flash differ, but the final destination remains the same in terms of organic search engine optimization. The scenario below reveals the basics of how Flash sites are typically optimized. In addition to the description, I included images to help further illustrate the dynamics involved.

“SEO for Flash” is simple in theory; embed an entire “site” within a Flash file and layer that Flash file over an interlinked (X)HTML structure of corresponding content pages via JavaScript. Thanks to the JavaScript (SWFObject), users with Flash enabled see Flash, while users without Flash enabled (previously Googlebot) receive the underlying interlinked (X)HTML version of content pages. In order to control the Flash presentation for users with Flash, URLs with #anchors are embedded to create the illusion of “seamless transitions” between “virtual pages” within the Flash file.
(A second iteration of this same technique draws text content seen both in the Flash presentation as well as the underlying (X)HTML from the server. However, Google does not attach external content resources loaded in Flash files. “If your Flash file loads an HTML file, an XML file, another SWF file, etc., Google will separately index that resource, but it will not yet be considered a part of the content in your Flash file.”)
While the scenario above seems fairly simple, understanding how each element is “digested” by Googlebot is a bit more complex. Here are a few issues to be aware of when optimizing Flash sites in light of the new Flash algorithm.
“Progressive Enhancement”
As illustrated by Case Study #1, Googlebot traverses simple JavaScript, like SWFObject and, as a result, it completely circumnavigates text content provided via “Progressive Enhancement” in most cases.
Flash in SERPs
As Case Study #1 and #2 illustrate, Google may not associate text content in Flash with the appropriate parent URL and/or as a single entity. This makes it possible for users without Flash-enabled browsers and/or devices (iPhone) to access Flash files directly from Google’s SERPs. This issue can result in a bad user experience.
Links
As illustrated by Case Study #3, Googlebot ignores pound signs (#anchors / fragment identifiers) in URLs. As a result, Googlebot interprets URLs containing pound signs as different URLs with different content than intended. (After pointing this issue out to the creators of SWFAddress, Asual added the “Copy link to clipboard” option to footer of pages in their SEO example.) This issue is further complicated by the introduction of Google’s new algorithm for Flash, the support for simple JavaScript and the possibility of Flash files being indexed in Google search engine results pages.
If a user posts a link to domain.com/photos.html#/contact.html, Googlebot will only see and index the content at domain.com/photos.html.
PageRank / Keyword Thinning
As illustrated by Case Study #2, Flash files can now accrue PageRank independent of their own parent URLs. As a result of this issue, PageRank thinning is likely to occur, because PageRank is divided between the parent URLs and actual URL. The percentage of thinning is likely to increase in proportion to the quantity of underlying (X)HTML pages containing “the flash file.”
Similar to PageRank, keyword relevancy may not be allocated to the intended URL. When keyword relevancy that is intended for one URL is instead allocated to another URL, thinning occurs.
Translation
As Case Study #4 illustrates, Google doesn’t seem to translate text content in Flash files, especially when text is supplied by a server or some other third party source.
Google SEO for Flash
Before talking about SEO for Flash, it’s important to define what that really means. Ask a Flash guy what SEO for Flash means and he might say something like “indexed content” or “indexation.” Ask an SEO guy what SEO for Flash means and he might say something like “ranking top 10 or text content in Flash.” As you can see, there are two different definitions and, therefore, two totally different expectations at work here. To an SEO, indexed content is the starting point where SEO for Flash begins. Simply “being indexed” is better defined as “Search Engine Friendly” (SEF). The introduction of Google’s Flash algorithm means most Flash sites are, by default, search engine friendly assuming text content resides within the Flash files and isn’t in a vector format.
Organic search engine optimization (SEO), unlike search engine friendliness (SEF), depends heavily on “meta data,” not just “meta tags.” Lots of information can be gleaned from (X)HTML by search engines via, TITLE elements, ALT attributes, images, headers (H1, H2, H3, H4…), internal link structure, fonts, link popularity, relationships, site categories, subdivisions and sections. Engines rely on these elements for meta data as well as other informational “signals” used for rankings. “More data is good data” but only when that data is available in a digital format that’s digestible by search engines and can be translated to determine relevancy for textual queries. As Vanessa Fox recently pointed out, the lack of structural meta data in Flash is a real disadvantage.
With Google’s introduction of “Universal search” in May 2007, Flash sites were dealt a new obstacle. Universal blends results from verticals like news, images and YouTube, in Google’s search results. The advent of “Universal search” is somewhat problematic for Flash sites, because Googlebot can’t extract images and/or video embedded in Flash for inclusion in Google’s “Universal” search results. To illustrate, currently Adobe.com doesn’t rank top ten in Google Images for [Adobe] or [Adobe logo].
Google Flash SEO Tips for 2009
Since “optimizing Flash” is difficult, it’s better to understand the fundamental limitations of the medium in terms of search, and to then concentrate on optimizing site design and architecture.
- When it comes to text, “Don’t use it for something when there’s already a standard whose output can be easily parsed, easily processed, and whose openness makes its processing easier for browsers and searchbots.” - “Bergy,” Google Webmaster Central
- Avoid text content and links in Flash
- Don’t use text content in Flash supplied via third party file
- If you must use text content in Flash, use sIFR
- If you must use text content in Flash and sIFR isn’t an option, create individual Flash files laid over each corresponding (X)HTML page via SWFObject
- “Instead of including everything in one flash file it may make sense to break the content into different flash files so you can create different HTML pages around the different ideas contained in it.” - Aaron Wall, SEOBook.com
- When using SWFObject, consider using absolute URLs in underlying (X)HTML and Flash files
- When using SWFObject, be sure to include “alternative” images for users without Flash
- Avoid using text content in Flash for pages employing “seamless transitions” where URLs don’t change, or, instead, include “pound signs”
- Provide links to important pages within Flash files using absolute URLs for users who arrive at the Flash file via Google search engine results pages
- Consider how translation issues may impact content in Flash and investigate ways of working around these issues